One hundred eighty-seven new packages made it to CRAN in April. Here are my picks for the “Top 40”, organized into ten categories: Biotechnology, Data, Econometrics, Machine Learning, Medicine, Science, Statistics, Time Series, Utilities, and Visualization.
Biotechnology
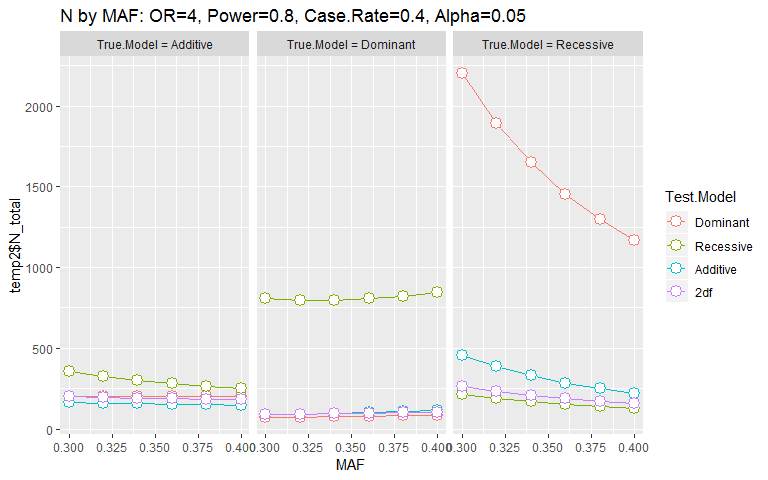
genpwr v1.00: Provides functions for power and sample size calculations for genetic association studies allowing for mis-specification of the model of genetic susceptibility. The methods employed are extensions of Gauderman (2002) and Gauderman (2002). See the vignette for details.
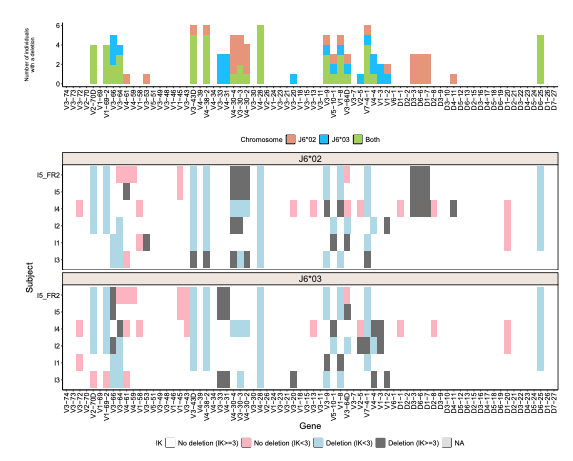
rabhit v0.1.1: Implements an adaptive Bayesian framework to infer V-D-J haplotypes and gene deletions from AIRR-seq data. See Gidoni et al. (2019) for background and the vignette for an introduction to the package.
Data
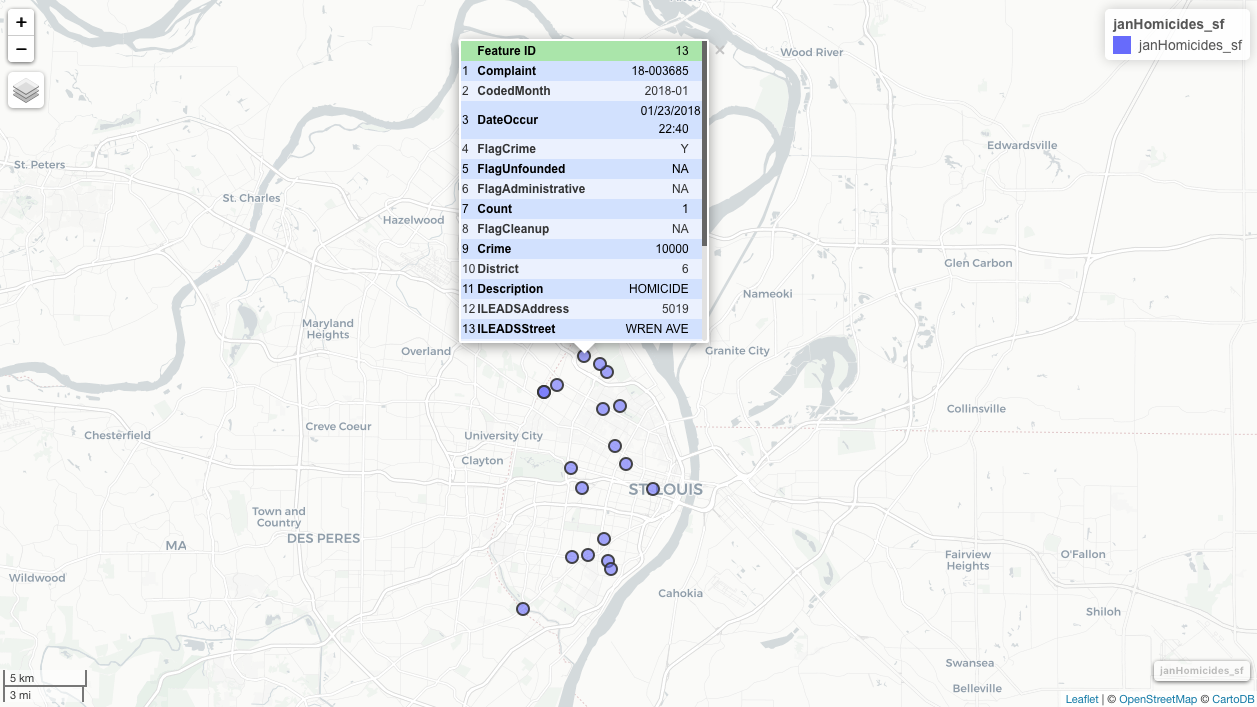
compstatr v0.1.1: Provides a set of tools for creating yearly data sets of St. Louis Metropolitan Police Department (SLMPD) crime data, which are available from January 2008 onward as monthly CSV releases. See the vignette.
DataSpaceR v0.6.3: Provides a convenient API interface to access immunological data within the CAVD DataSpace, a data sharing and discovery tool that facilitates exploration of HIV immunological data from pre-clinical and clinical HIV vaccine studies. There is an Introduction.
ebirdst v0.1.0: Provides tools to download, map, plot and analyze eBird, a global database of bird observations collected by citizen scientists, Status and Trends data. There is an Introduction and vignettes on Generating maps and stats, Data Structure, and Predictor Performance, Directionaly and Performance Metrics
PropublicaR v0.9.2: Provides wrapper functions to access the ProPublica’s Congress and Campaign Finance APIs.
tradestatistics v0.2: Provides access to the Open Trade Statistics API from R to download international trade data. There is an Introduction and a vignette on data sets.
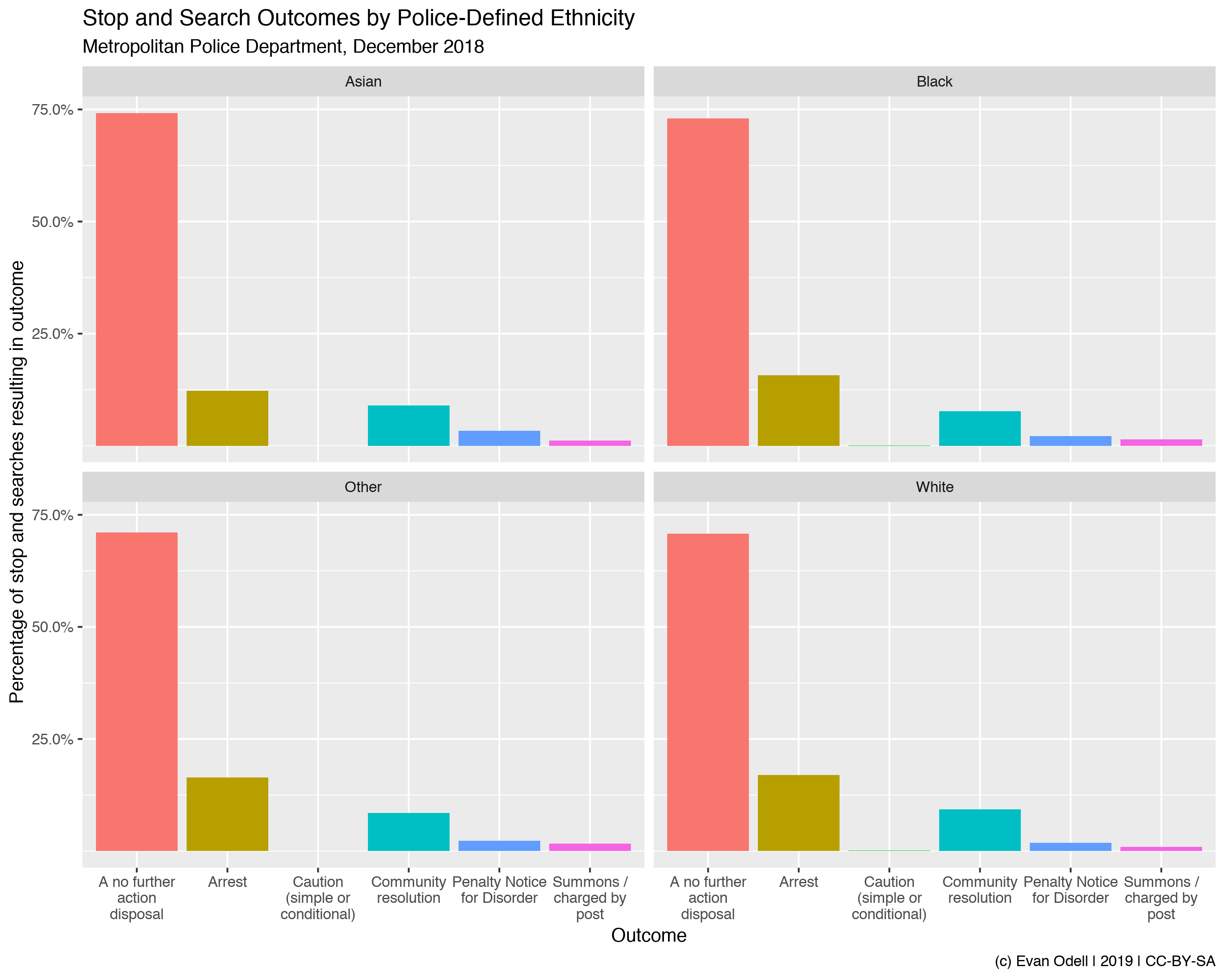
ukpolice v0.1.2: Provides access to UK Police public data, including data on police forces and police force areas, crime reports, and the use of stop-and-search powers. See the vignette for details.
Econometrics
modelplotr v1.0.0: Provides plots to assess the quality of predictive models from a business perspective, which can show how implementing the model will impact business targets like response on a campaign or return on investment. See the vignette for examples.

SortedEffects v1.0.0: Implements the estimation and inference methods for sorted causal effects and classification analysis as described in Chernozhukov et al. (2018). See the vignette for an introduction and example.
Machine Learning
iBreakDown v0.9.6: Implements Break Down Tables and Plots, which are model-agnostic tools for the decomposition of predictions from black boxes. The methodology behind it is described in Gosiewska and Biecek (2019). There are vignettes for classification models, regression, and an Example.
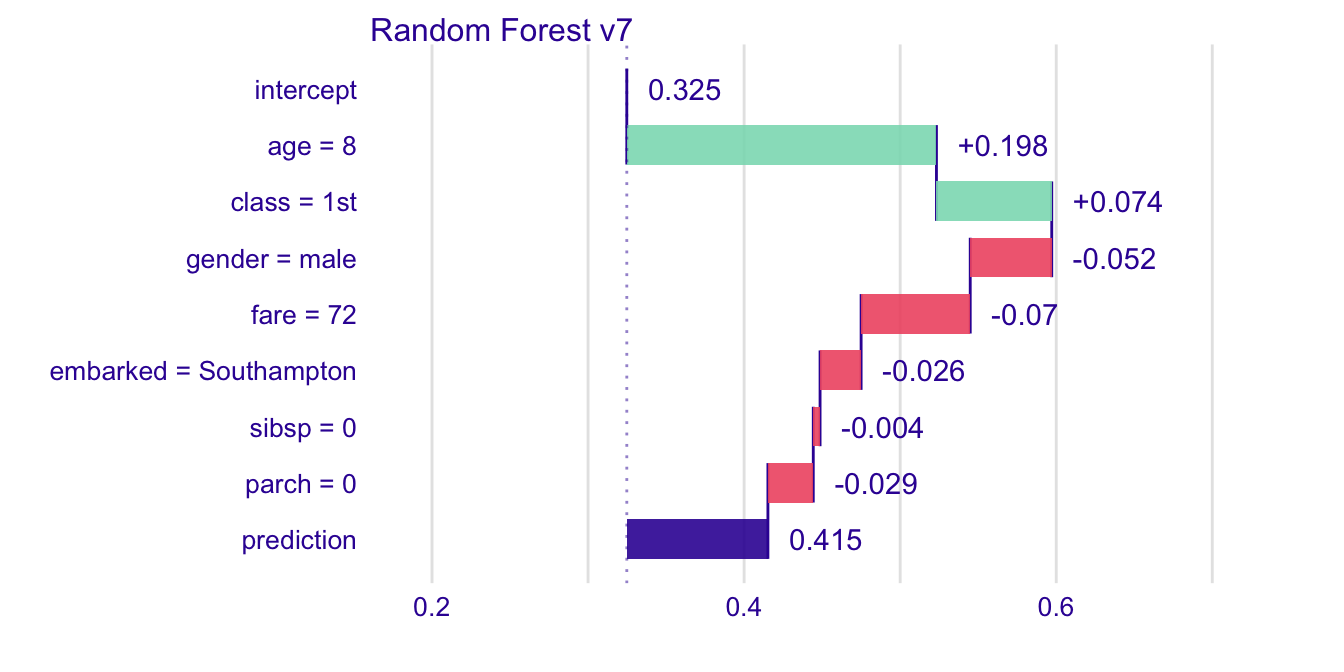
localModel v0.3.11: Provides local explanations of machine learning models, and describes how features contributed to a single prediction. See Ribeiro & Singh (2016) for details. There is an Introduction and vignettes on Methodology and Explaining Classification Models.
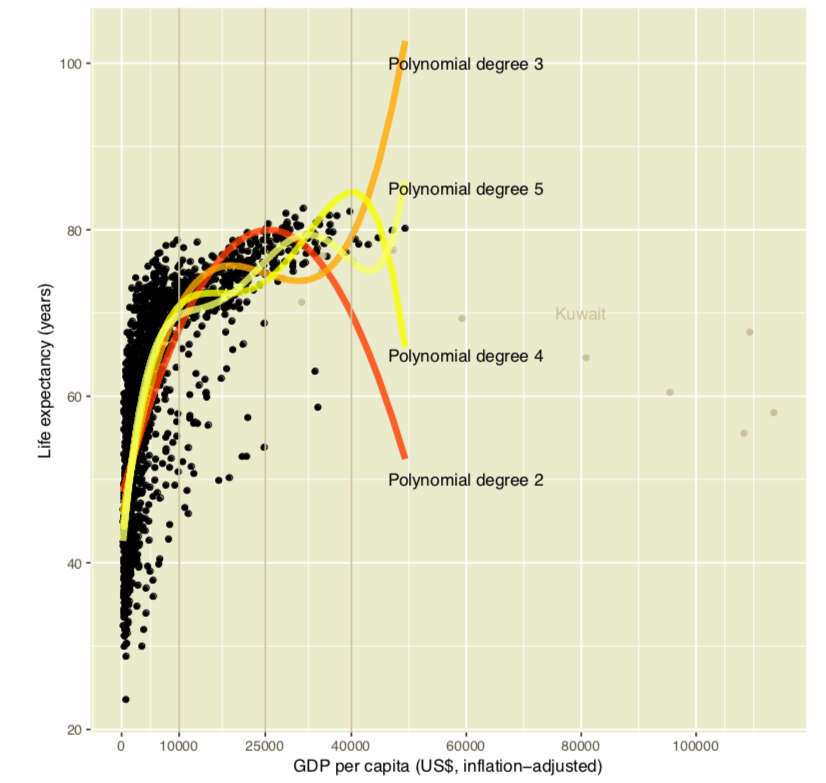
polyreg v0.6.4: Automates the formation and evaluation of polynomial regression models, and provides support for cross-validating categorical variables. See Cheng et al., and look here for examples.
rfVarImpOOB v1.0: Estimates variable importance for random forests by computing impurity reduction importance scores for out-of-bag (OOB) data, complementing the existing in-bag Gini importance. See Strobl et al (2007), Strobl et al (2007), and Breiman (2001). The vignette contains a small example.
rsparse v0.3.3.1: Implements several algorithms for statistical learning on sparse matrices, including matrix factorizations, matrix completion, elastic net regressions, and factorization machines. Look here for an example.
Medicine
blockRAR v1.0: Provides functions to compute power for response-adaptive randomization clinical trial with a block design that captures both the time and treatment effect. See [Chandereng & Chappell (2019)](arXiv:1904.07758 for details and the vignette for Bayesian and Frequentist examples.
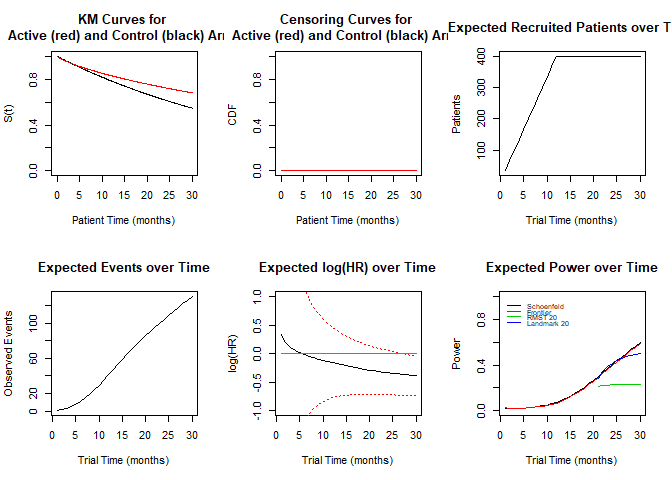
gestate v1.3.2: Provides tools to assist planning and monitoring of time-to-event trials under complicated censoring assumptions and/or non-proportional hazards. There are vignette on Predicting Events and Planning Trials.
Science
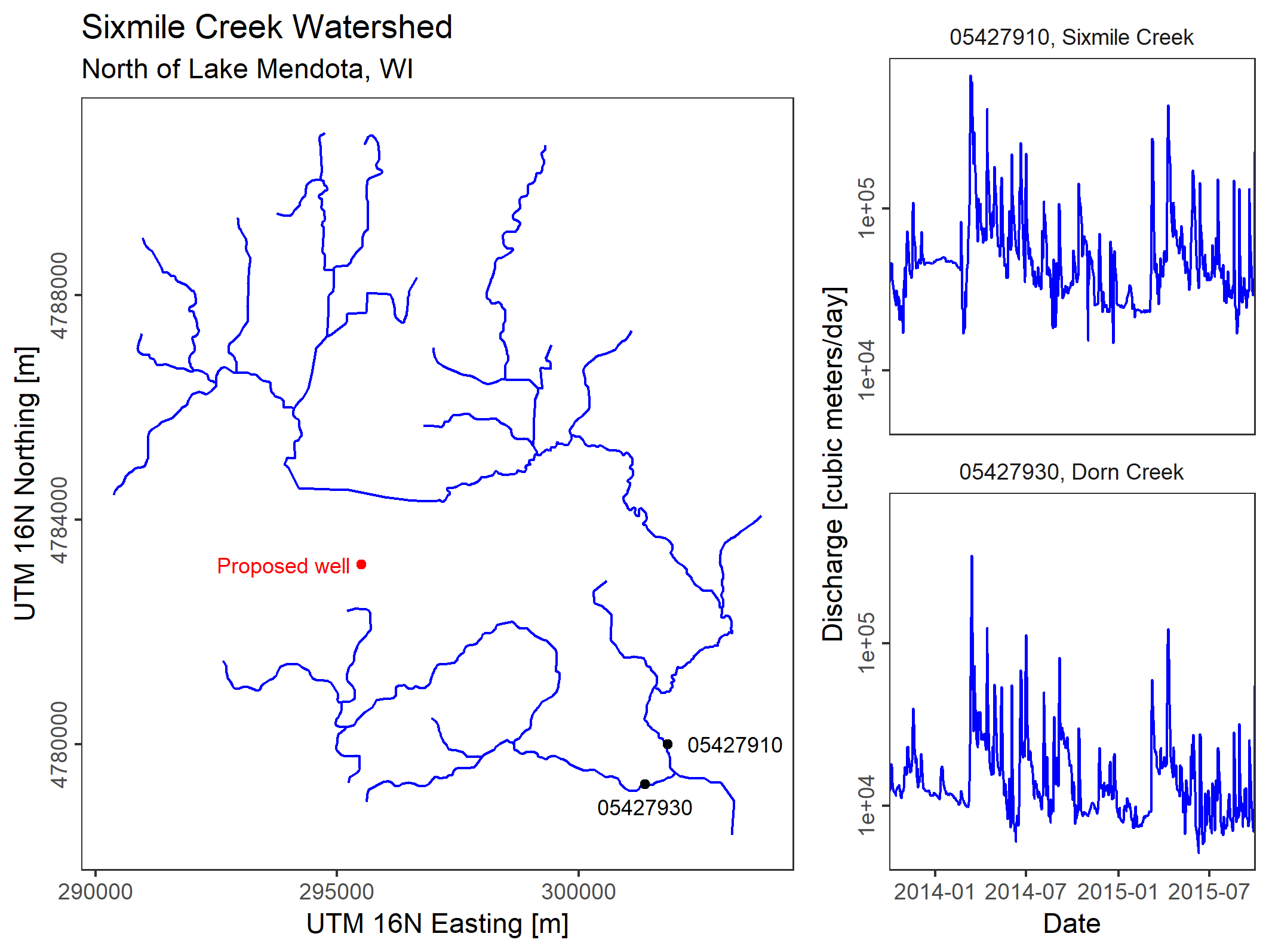
streamDepletr v0.1.0: Implements analytical models for estimating streamflow depletion due to groundwater pumping, and other related tools. See Zipper et al. (2018) for more information on depletion apportionment equations, and Zipper et al. (2019) for more information on analytical depletion functions. There is a vignette.
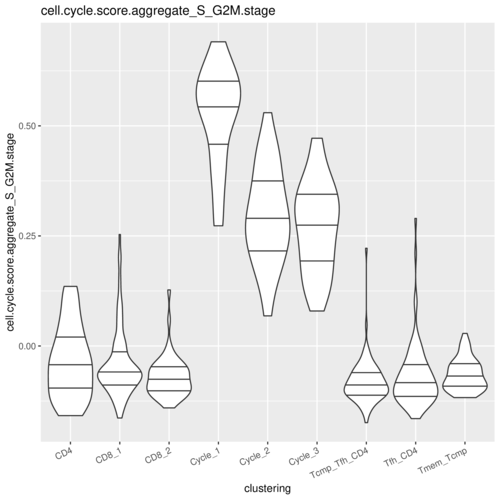
RobustSingleCell v0.1.1: Implements functions for the robust single cell clustering and comparison of population compositions across tissues and experimental models via similarity analysis. See Magen (2019) for details and the vignette for examples.
Statistics
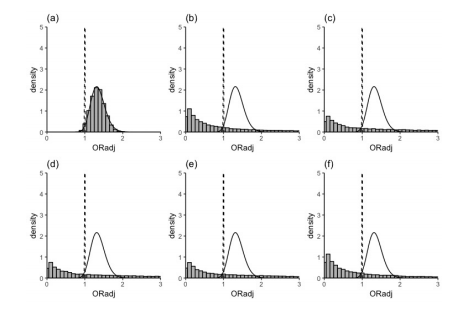
BayesSenMC v0.1.1: Provides functions to generate different posterior distributions of adjusted odds ratio under different priors of sensitivity and specificity, and plots the models for comparison. See Chu et al. (2006) and Chu et al. (2010) for background.
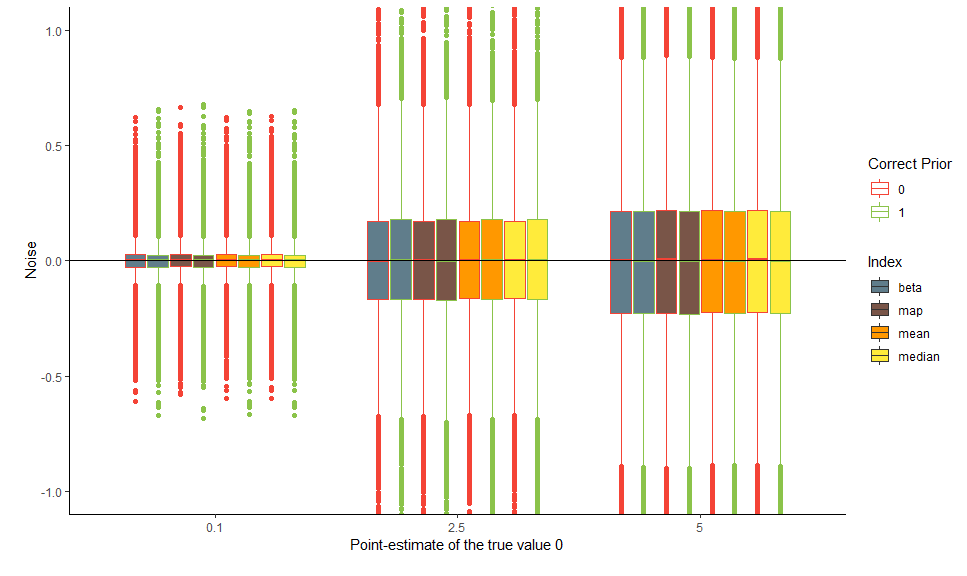
bayestestR 0.1.0: Provides utilities to describe posterior distributions and Bayesian models, and the vignette for details and examples. There is a Getting Started Guide, and vignettes on Comparison of Point Estimates, Comparison of Indices, and Examples.
CoSMos v1.0.1: Implements a framework unifying, extending, and improving a general-purpose modelling strategy, based on the assumption that any process can emerge by transforming a specific ‘parent’ Gaussian process. See Papalexiou (2018) and the vignette.
fic v1.0.0: Provides functions to determine how well different models fitted by maximum likelihood estimate a quantity of interest, including generalized linear models and parametric survival models. See Claeskens and Hjort (2003) for details. There is an Introduction along with vignettes for Linear regression, loss functions, multi-state models, skew normal models, and survival models.
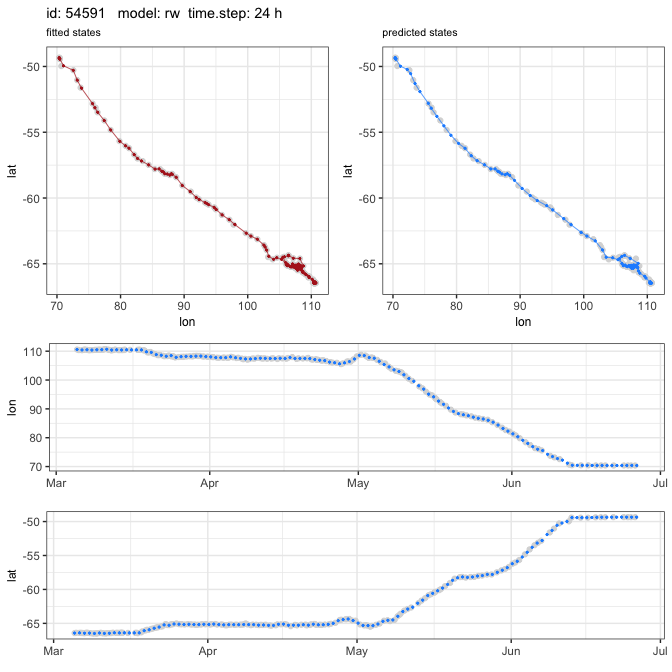
foieGras v0.2.1: Provides functions to fit continuous-time state-space models for filtering Argos satellite (and other) telemetry data. The vignette provides an overview.
glmaag v0.0.6: Implements efficient procedures for adaptive LASSO and network regularized for Gaussian, logistic, and Cox models. See Ucar, et. al (2007) and Meinshausen and Buhlmann (2006) for a discussion of network estimation procedures. The vignette provides an example.
Irescale v0.2.6: Provides a scaling method to obtain a standardized Moran’s I measure for the spatial autocorrelation of a data set, which gives a measure of similarity between data and its surrounding. See Chen (2009) for the method of calculation and the vignette for an example.
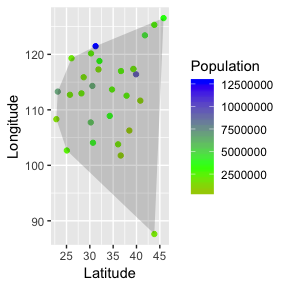
mvgraphnorm v1.81: Provides a function to compute a constrained covariance matrix for a given graph to generate samples from a Gaussian graphical model, using different algorithms for the analysis of complex network structure. See Kim et al. (2008) and Speed et al. (1986) for algorithms, and the vignette for an example.
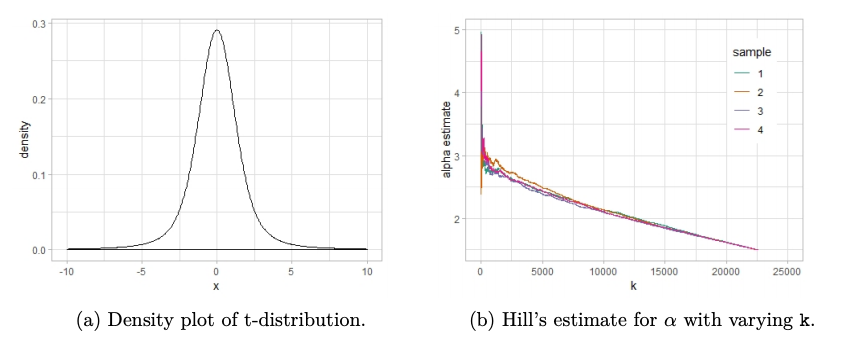
ptsuite v1.0.0: Implements several methods for tail index estimation for power law distributions, including maximum likelihood Newman (2005), Hill’s estimator Hill 1975, least squares Zaher et al. (2014), method of moments Rytgaard (1990), and percentiles Bhatti et al. (2018). There is a vignette.
spatialreg v1.1-3: Provides a collection of functions for fitting functions for spatial cross-sectional models on lattice/areal data using spatial weights matrices. There is a vignette on Moran Eigenvectors and another on the North Carolina SIDS data set.
Time Series
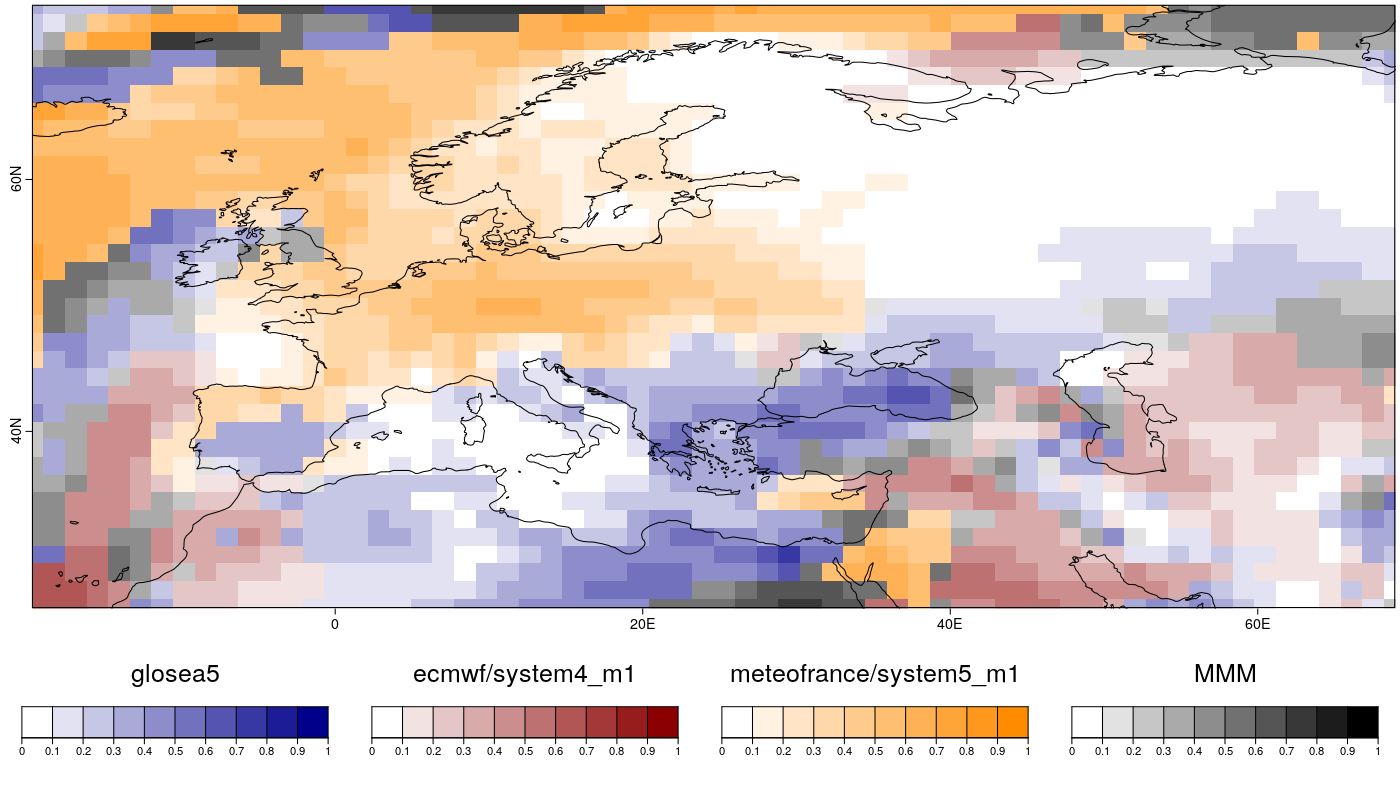
CSTools v1.0.0: Implements process-based methods for assessing climate forecasts, including forecast calibration, bias correction, statistical and stochastic down-scaling, optimal forecast combination, and multivariate verification. See Doblas-Reyes et al. (2005), Mishra et al. (2018), Terzago et al. (2018), Torralba et al. (2017), and D’Onofrio et al. (2014) for details. There are vignettes on Multi Model Skill Assessment, Multivariate RMSE, and the RainFarm Model.
DChaos v0.1-1: Implements several algorithms for detecting chaotic signals inside univariate time series using methods derived from chaos theory, which estimate the complexity of a data set through exploring the structure of the attractor. See Ruelle and Takens (1971) for some deep background.
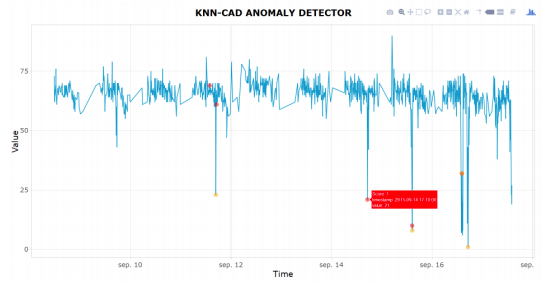
otsad v0.1.0: Implements a set of online fault detectors for time-series, including PEWMA Carter et al. (2012), SD-EWMA and TSSD-EWMA H. Raza et al. (2015), KNN-CAD Burnaev et al. (2016), KNN-LDCD Ishimtsev et al. (2017), and CAD-OSE M. Smirnov (2018). There is a vignette.
Utilities
inspectdf v0.0.2: Provides a collection of utilities for column-wise summary, comparison, and visualization of data frames. Functions report missingness, categorical levels, numeric distribution, correlation, column types, and memory usage. See README for examples.
suppdata v1.1-1: Provides functions for downloading data supplementary materials from manuscripts, using papers’ DOIs as references. Facilitates open, reproducible research workflows: scientists re-analyzing published data sets can work with them as easily as if they were stored on their own computer. There is a brief Introduction.
tidync v0.2.1: Provides tidy tools for working with NetCDF data sources. The vignette provides background and describes data extraction and exploration.
tinytest v0.9.3: Provides a lightweight (zero-dependency) and easy to use unit testing framework. Main feature: install tests with the package. The vignette shows how to use the package.
Visualization
frequentdirections v0.1.0: Implements frequent-directions algorithm for efficient matrix sketching. See Edo Liberty (2013) for details and the README for examples.
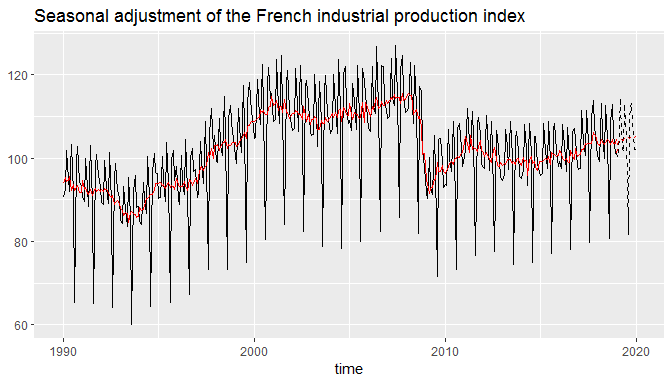
ggdemetra v0.1.0: Provides ggplot2 functions to return the results of seasonal and trading-day adjustment made by RJDemetra, the seasonal adjustment software officially recommended to the members of the European Statistical System and the European System of Central Banks. The vignette provides examples.
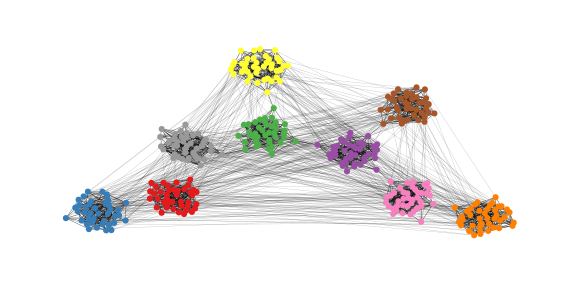
graphlayouts v0.1.0: Implements several new layout algorithms to visualize networks. Most are based on the concept of stress majorization by Gansner et al. (2004). The vignette shows several examples.
tidymv v2.1.0: Provides functions for visualizing generalized additive models and getting predicted values using tidy tools from the tidyverse packages. There is a vignette for Plotting Model Predictions and another for Plotting Smoothing Curves.
You may leave a comment below or discuss the post in the forum community.rstudio.com.